|

Indonesia
Internet eXchange Points
Network Access Point
since August,
1997
Updated:
December, 1998
TECHNICAL DESIGN AND
CONFIGURATION
APJII - iIX TEAM
http://www.apjii.or.id
APJII-iIX Engineering
Team - 2nd
Edited "xxx" in
this document by all means to ensure the confidentiality of APJII - IIX
security matters
INTRODUCTION
The Indonesian Internet eXchange (iIX) is a
collaborative project sponsored by APJII. It's overall objective is the
keep all intra-Indonesian Internet traffic within Indonesia. The iIX will
obsolete the old method of using the US and other countries to exchange
intra-Indonesian Internet traffic. iIX creates the foundation for a
comprehensive national Internet infrastructure where all ISP collaborate
for the common good.
TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
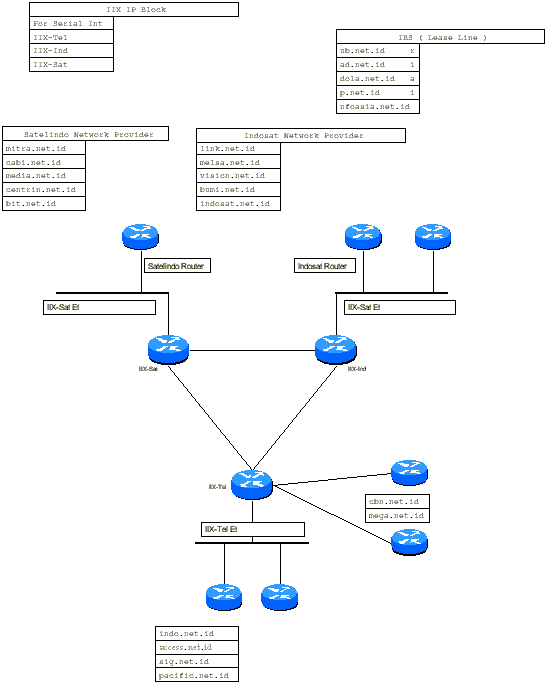
The iIX interconnects three different sites to
make one large IXP. The three sites are Telkom Indonesia, SatelIndo, and
Indosat. ISPs can choose which site to connect based on circuit
availability, upstream customer relationships, or organizational
preference.
IPv4 Address Plan
IPv4 addresses have been assigned from the
IANA IXP coordinator - Bill Manning. One /24 has been assigned for
the entire IXP. Hence, CIDR compliance is required for any router or
switch connecting to the IXP and all ISP's equipment working with the iIX.
198.32.xxx.xxx/24 has been assigned.
The following is a break down of
the assignments in the iIX (current on the data of this document) :
|
IP Address
Block |
Assignment |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/28 |
Loopback
Interfaces on the routers |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Telkom
Loopback Interface |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Satelindo
Loopback Interface |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Indosat
Loopback Interface |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/28 |
Point to Point
Serial Links ( 4 x /30s) |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/30 |
Telkom <->
Satelindo Link |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/30 |
Telkom <->
IndoSat Link |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/30 |
Satelindo
<-> IndoSat Link |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/27 |
Point to Point
Serial Links ( 8 x /30s) |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/30 |
CBN.net.id
Link |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/30 |
MEGA.net.id
Link |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/26 |
Telkom IX Medium
(ethernet) |
| 198.32xxx.xxx |
iIX-Tel Router
Ethernet port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Indo.net.id's
router ethernet port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Pacific.net.id's
router ethernet port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Traffic
Probe |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Logging &
Configuration Server |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/26 |
IndoSat IX
Medium (ethernet) |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
iIX-IND Router
Ethernet Port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Indosat's
Customer Router Ethernet Port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Indosat's Core Router Ethernet Port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
RADNet Core
Router Ethernet Port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
UBNet Core Route
Ethernet Port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Traffic
Probe |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Logging &
Configuration Server |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx/26 |
Satelindo IX
Medium (Ethernet) |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
iIX-SAT's router
ethernet port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Satelindo's
router ethernet port |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Traffic
Probe |
| 198.32.xxx.xxx |
Logging &
Configuration Server |
| End |
End |
Autonomous Systems Number
[ASN]
ASxxxx has been delegated from APNIC for the
iIX. This will be used across the IXP for inter-IXP traffic (between the
three sites) and with IXP members (in route reflector mode) who have not
yet received their own ASN from APNIC. All IXP members are encouraged to
get their own ASN.
Route Filtering via
BGP
Filtering routes via BGP is necessary to
enforce the IXP's peering policy and to protect the members of the IXP
from unwanted routes. Two filtering techniques are used in this
configuration: AS Path Filters and Distribute Lists Filters.
AS Path Filters
AS Path Filters will be used to enforce the
policy for the IXP. Only the ASNs with belong to the members of the IXP
will be distributed to the IXP members. This explicit permit rule will,
by default, deny ASNs which are not explicitly permitted in the AS Path
Filter. This prevents routes leaking from one provider from being
propagated across the IXP. For example, if provider A was connected to
Internet MCI (AS3561) in the US, and for some reason Internet MCI's
routes leaked through provider A, then the AS Path Filters would block
AS3561 since they are not explicitly in the AS Path list.
In addition, the AS Path filters will use a
format that will only accept routes that originate from the ISP peering
to the IXPs. For example, _xxxx$ will only allow routes which originate
in ASxxx. Any routes that originate outside of ASxxx (for example
Internet MCI) will be denied.
Lastly, the AS Path filters will be applied
on all outbound BGP peers for both the IBGP route reflector connections
(for those ISPs with their ASN) and the EBGP peer connections (for those
ISP with their ASN). AS Path filters will also be applied on all EBGP
inbound connections.
Distribute List Filters
Distribute List filters will be used to
remove RFC 1918 (Private Address Space), multicast, and other routes
that should not be propagated on the Internet routing table (i.e. like
127.xxx.xxx.xxx/16). This safe guard keeps networks link
10.xxx.xxx.xxx/8 from getting leaked out across the
Internet.
IP Filtering
IP filtering is an additional policy
enforcement tool. Essentially, you place a egress and ingress ip packet
filter on the peer connections connecting to the IXP. Every packet
coming into or out of the IXP will get checked. Some filters are
designed to insure that all packets that leave a ISP belong to that ISP.
This called ingress filtering. Other filters check packets coming
into a ISP are not "rouge," private, or spoofed addresses. This is
called egress filtering. ISPs who connect to an IXP are
encouraged to do both.
Connecting to the IXP
iIX will have several types of ISPs
connecting to the IXP fabric. Some ISPs will have their own Autonomous
System Numbers (ASNs) and will peer directly to the IXP. Other ISPs will
peer directly, but have yet obtained a ANS. These will connect via BGP
route reflectors within the iIX's own ASN. Still others will connect
through the commercial Layer 3 IXPs of Indosat and Satelindo. All of
these ISPs will have to integrate BGP into their internal network
routing topology. This section's goal is to highlight some of the design
and integration options available to the ISP connecting to the
iIX.
ISPs with no ASN
Some ISPs will not have their own ASN. The
are connected to the Internet via a lease line to a Network Service
Provider (NSP) in the US. Their internal routing could be built with
static routes, OSPF, IS-IS, EIGRP, or RIPv2. What follows is one example
of a way a ISP can configure their routing protocols.
BGP to OSPF to BGP
ISPs who are already using BGP to connect to
the Internet should not have any problem connecting to iIX. Due
consideration must be paid to the filters used. ISPs should insure that
iIX routes are not leaked to the rest of the Internet and routes from
the Internet are not leaked into iIX. Figure 5 is a diagram of an ISP
(AS 100) with connections to two upstream NSPs (AS 200 & AS 300).
EBGP is used to advertise the ISP's route objects to iIX, NSP2 and NSP3.
The full Internet routing table is pulled from the two
NSPs.
Proactive filtering is a must in this
situation. Config Example 3 is one example of BGP filtering that would
satisfy the requirements the filtering requirements. Note that the
as-path access-list 3 filters routes that originate in AS 100. This is
to prevent routes advertised out one NSP from coming back through the
other NSP.
Other filter rules will also work. Refer to
the documentation on BGP Regular Expression filters.
iIX Detailed Diagram:
Phase-1
| 
